Autism
Autism is a neuro-developmental disorder which is defined by deficits in social reciprocity and communication, and by unusual restricted, repetitive behaviors. It begins in early childhood and characterized by qualitative impairment in communication skills, social interactions and reciprocity, imagination and play. Autism Spectrum Disorders can be explained under the disease Unamada in Ayurveda. The majority of clinical features of different varieties of Autism Spectrum Disorders resemble features of Vatika and Kaphaja dominant Unamada.
Brief with types
The classification of Autism Spectrum Disorders has undergone many revisions with progression of knowledge and time. At present, the diagnosis of Autism spectrum brings all similar disorders with Autistic features under one umbrella. The Autism Spectrum Disorders include the following conditions.
- Autistic disorder
- Asperger Syndrome
- Rett Syndrome
- Pervasive Developmental Disorder- Not Otherwise Specified (PDD-NOS)
- Childhood Disintegrative Disorder (CDD)
Earlier Autism was included under the broader category of Pervasive Developmental Disorders. The term Pervasive Developmental Disorders refers to a group of disorders characterized by abnormalities in communication and social interaction and by restricted repetitive activities and interests.
Signs & Symptoms(Lakshana):
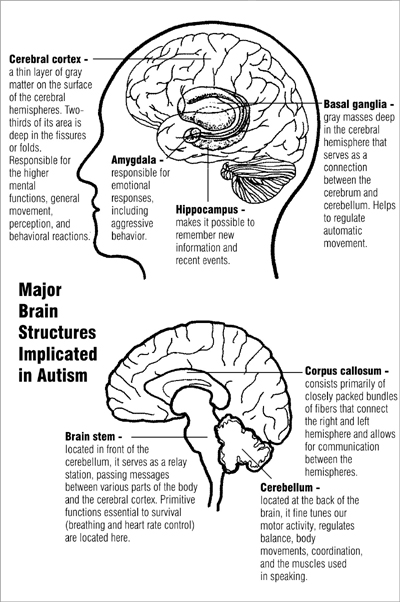
Clinical Features of Autism Spectrum Disorders Social interactions and relationships:
- Lack of eye contact and facial expressions
- Lack of joyful expressions
- Lack of gestures
- Lack of sharing of enjoyment
- Lack of response to name
- Lack of interest in other children, prefers to play alone
- Lack of sharing enjoyment or achievements with other people
- Failure to form close relationships with peers or children of same age
- Abnormal body posture
- Unaware of other's feelings or distress such as pain or grief
- Difficulty seeing other's point of view
- Treating others as objects or tools
Verbal and nonverbal communication:
- Delay in speech or lack of learning to talk
- Problems in taking steps to start a conversation
- Stereotyped and repetitive use of language
- Echolalia
- Difficulty understanding listener's perspective like meaning. Humour etc
Limited interests in activities and restricted and repetitive behaviours:
- An unusual focus on parts of an item such as toy
- Preoccupation with certain items or topics
- Lining up toy or focused with only 1part of a toy (e.g., spinning wheels)
- Limited or lack of pretend play
- A need for sameness and routines such as eating same food or preferring same route for travel
- Stereotyped behaviours - Repetitive hand flapping, rocking, or spinning movements
- Intense interests in certain topics such as chemicals, vehicles etc.
- Distress with small changes to the routine
- Hypo- or hypersensitivity to sensory stimuli such as distress with loud noises or light smell)
- Hyperactivity
- Impulsivity
- Attention deficit - short attention span
Associated problems
- Mental retardation
- Physical clumsiness
- Seizures
- Gastrointestinal problems such as constipation, abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, or nausea
- Mood disorders
- Anxiety problems
- Phobias or excessive fears
- Transition-related stress
- Excessive startle
- Obsessions and compulsions
Causes(Nidan):
The causes of ASD are still controversial. Genetic susceptibility as well as environmental trigger factors are considered as the most possible ones.
The causes of Autism (Unmada) in Ayurveda can be summarized into the following headings:
- Beejadosha (Genetic alteration, mutation)
- Aharadosha (Food related causes) such as Viruddhahara (incompatible foods).
- Viharadosha (Inappropriate regimens)
- Manaabhighata (Brain injury)
- Vaikarikabhava such as Bhaya, kopa, soka and harsha (Emotional factors such as fear, anger, sorrow, pleasure etc)
Treatments:
Autism Spectrum Disorders can be explained under the disease Unmada. The majority of clinical features of different varieties of Autism Spectrum Disorders resemble features of Vatika and kaphaja dominant Unmada.
The rational Ayurveda treatment is carried out in four parts. They are:
- Dosha pacifying therapy (Samsamana),
- Bio-cleansing therapy (Samsodhana or Panchakarma)
- Avoidance of causative factors (Nidana Parivarjana)
- Favourable diet and regimens (Pathya Ahara vihara)
Autism requires therapies which work at the physical, mental and spiritual planes. Classical Ayurvedic treatment recommended for Unmada (Psychological disorders in general) is well suited to bring back children affected with Autism Spectrum Disorders to normalcy.
The classical Ayurvedic management of Unmada is as follow:
- Deepana and Pachana (Drugs and procedures that promote digestion)
- Snehapana (internal oleation use of medicated ghee)
- Mridu shodhana (mild body purification by emesis or purgation)
- Niruhabasti (decoction enema) and Snehavasti (oil enema)
- Sirovirechana or Nasya (medicated nasal drops)
- Sanjnaprabodhana (oral medication to stabilize the mind)
Apart from the modified Panchakarma therapies, certain procedure based therapies are also used in the management of Autism Spectrum Disorders. These are mainly used to promote the development of brain and to reduce or control the troublesome behaviours found with Autism Spectrum Disorders.
- Abhyangam (Oil massage-head and body)
- Siropichu (Overhead application of specific oil)
- Sirodhara (Pouring of specific oil over forehead as a continuous stream)
- Sirolepam (Overhead application of medicinal paste)
- Takradhara (Pouring of medicated buttermilk over forehead as a continuous stream)
Additional Treatment
Intensive, sustained special education programs and behavior therapy early in life can help children acquire self-care, social, and job skills, and often improve functioning and decrease symptom severity and maladaptive behaviors, claims that intervention by around age three years is crucial are not substantiated.
Available approaches include
- Applied behavior analysis (ABA)
- Developmental models
- Structured teaching
- Social skills therapy
- Occupational therapy
Among these approaches, interventions either treat autistic features comprehensively, or focalize treatment on a specific area of deficit.
Prevention
An Ayurveda dominant pre conception care and life style of marrying partners, a pre, post and neonatal care of pregnant woman, foetus and newborn as well as prescribed daily routines, seasonal care and ethical regimens shall pave way for preventing and eliminating Autism Spectrum Disorders and the like from the society.
Diets and actions contraindicated are,
- Alcohol
- Purgent and spicy food
- Penetrative and irritant food
- Irritating insulting incidences and activities
- Suppression of natural urges
- Incompletible and polluted food
- Sleeplessness